Alopecia, or alopecia (lat.), is a general medical term for excessive hair loss. Different forms of alopecia, or hair loss, can have different causes and symptoms.
Hair loss can be tough to deal with, and there are different forms of a condition called alopecia. Each type affects people in unique ways, making it important to understand what they are.

- Alopecia Areata: This form often starts suddenly and causes small patches of hair to fall out. It can happen to anyone, regardless of age gender. For many, it’s surprising and even upsetting because the hair usually comes back over time, but not always in the same way.
- Alopecia Totalis: This is a more severe type where all the hair on the scalp is lost. Imagine waking up one day and noticing that your head is completely bare! It’s a huge change and can impact how someone feels about themselves.
- Alopecia Universalis: The most extreme form, alopecia universalis leads to losing all body hair, including eyebrows and eyelashes. This can feel overwhelming for those who experience it, affecting their self-esteem and everyday life.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is common among adults. It happens gradually and is often linked to genetics. For some, seeing thinning hair can cause stress or worry
We know the following forms of alopecia:
Table of Contents
The most common forms are:
- Androgenic alopecia: male and female pattern baldness
- Alopecia areata: limited hair loss
- Traction alopecia: hair loss caused by long-term physical stress
Other forms of alopecia:
- Alopecia totalis
- Alopecia Universalis
- Scarring alopecia
- Anagen effluvium
- Telogen effluvium
Male and female baldness—androgenic alopecia
Male pattern baldness is the most common form of hair loss that affects millions of men worldwide. It most often manifests itself in the late twenties or early thirties of a person’s life. Statistics say that every second man after reaching the age of fifty suffers from alopecia.
The so-called pattern or pattern by which hair recedes from the head and thus creates the typical hairline of baldness is the same for most men. Loss of hair on the top of the head, a receding line from the forehead, or the so-called corners on the sides of the head are common.
Male pattern baldness is hereditary. This means that if someone in your family suffers from this disease, it may affect you as well. Male baldness is determined by genetics up to 90%.
Androgenic alopecia in women
Just as this unpleasant disease can affect men, it can also afflict women. In women, alopecia most often occurs in the form of so-called diffuse hair thinning. A typical manifestation is a translucent skin of the scalp in places on the crown, or sparse paths or places where hair strands divide.
It is not known whether female alopecia is also hereditary. Its causes are less known. However, it usually occurs after menopause.
Androgenic alopecia is discussed in more detail in the section below.
OUR TIP: TESTED AND EFFECTIVE AGAINST ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA WITHOUT SIDE EFFECTS!
- Supports healthy hair growth
- Restores new hair growth
- Gentle, without side effects or irritation
- Also suitable as an accompanying treatment with minoxidil
IN ADDITION TO ANDROGENIC ALOPECIA, THERE ARE OTHER FORMS OF ALOPECIA:
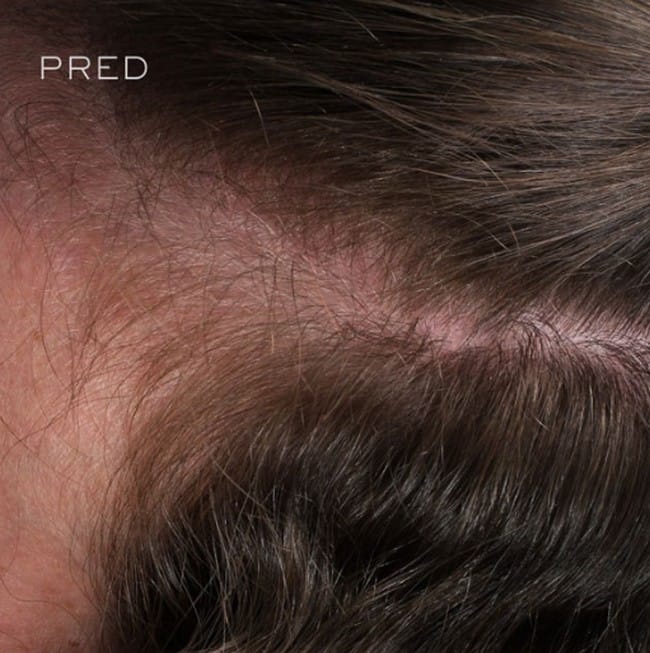
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that causes focal hair loss. Hair loss usually affects the scalp, but it can also occur in other areas of the body.
What are the causes?
The exact causes of alopecia areata are not fully known, but it is believed to be caused by the body’s immune system attacking hair follicles. In some cases, it can also be the result of general stress on the body.
This form of alopecia manifests itself as hair loss in irregular clumps and can also lead to complete loss of hair and body hair. However, spontaneous remission occurs in some patients (even without treatment).
Symptoms of alopecia areata
The main symptom of alopecia areata is hair loss in the so-called bearings. Hair usually falls out in the form of small or large round spots on the scalp. These bald spots are usually a few centimeters or less in extent. In the early stages, you may notice clumps of hair on your pillow or in the shower.
However, other types of diseases can also cause this form of hair loss. These include thyroid disease, nutritional deficiencies, and stress.
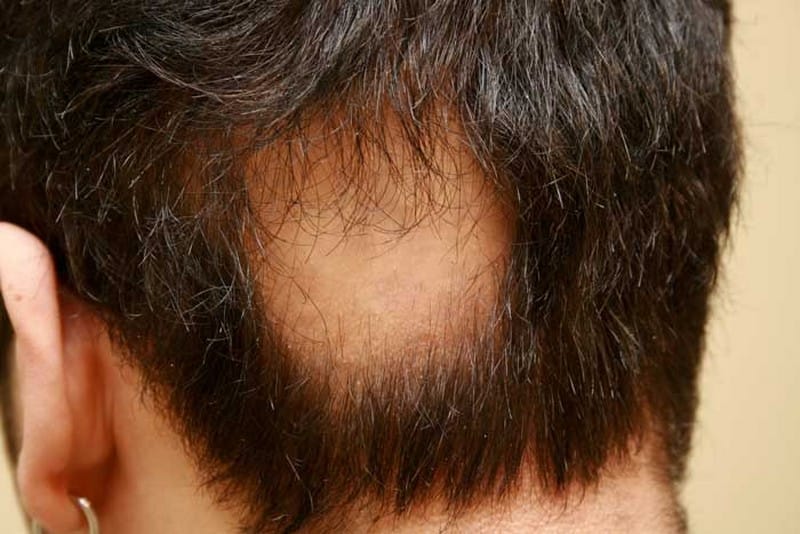
Diagnostics
Hair loss alone is not enough to diagnose alopecia areata. Hair can grow back at any time and then fall out again. The extent of hair loss and regrowth varies greatly from person to person.
Is it contagious?
Alopecia areata is not contagious. It is caused by the immune system attacking and destroying hair follicles, causing hair loss. This disease most often occurs in otherwise healthy people.
How to treat it?
Alopecia areata occurs in both men and women at any age. It most often occurs in people who have a family history of autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis. Unfortunately, treatment is still problematic and the disease is often resistant to therapy.
A hair thickener is a suitable solution for alopecia areata!
- The most popular hair thickener in the world!
- Natural result in a few seconds
- Resistant to rain, wind, and sweat
- In 10 natural color shades
Nanogen fibers before and after
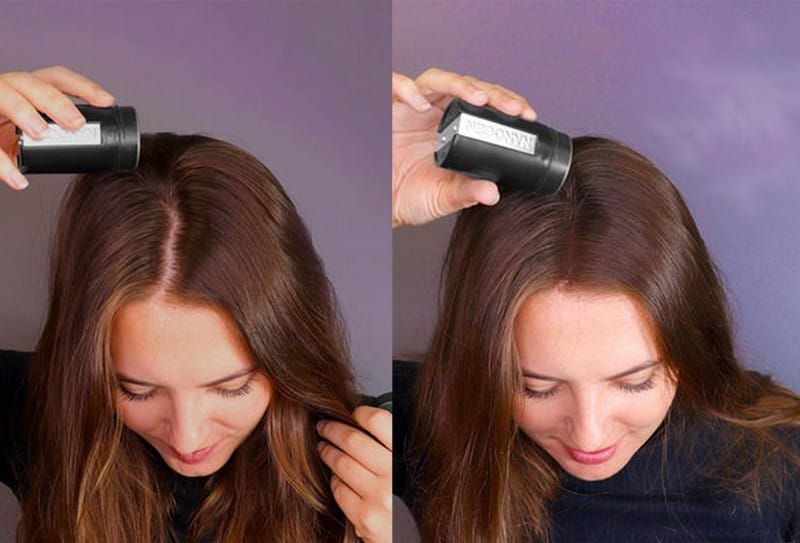

For many people with alopecia areata, hair thickeners, and hair straighteners are especially helpful because their hair loss is usually only temporary. Hair thickeners come with a solution that is affordable, immediate, and at the same time relieves a person’s stress caused by the situation, which can significantly contribute to recovery.
Traction alopecia
It is the result of long-term physical stress on the hair. Traction alopecia is mainly observed in people with long hair. Traction alopecia can be caused by wearing certain hairstyles that stress the hair, tight braids, and braids.
As soon as the mentioned factors are eliminated in a person, this form of hair loss usually disappears.
Alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis
Alopecia totalis means complete loss of hair on the head, and Alopecia universalis results in complete loss of hair and body hair. These forms of hair loss are the most visible and so far there is no cure for them. Many patients suffering from this form of alopecia invest in wigs and hairpieces.
There are many other causes of hair loss or diffuse hair thinning, from certain diseases, hormonal imbalances, and skin characteristics, to the consequences of medical treatment.
If you are interested in the causes of your hair loss, you should ask your doctor for advice.
!!! And now back to androgenic alopecia – IMPORTANT !!!
Androgenetic or androgenic alopecia—the so-called pattern of male and female hair loss is referred to this way because of the already known – predictable scheme of the “pattern” of hair loss, marked on the so-called Norwood scale for men and the Ludwig scale for women.
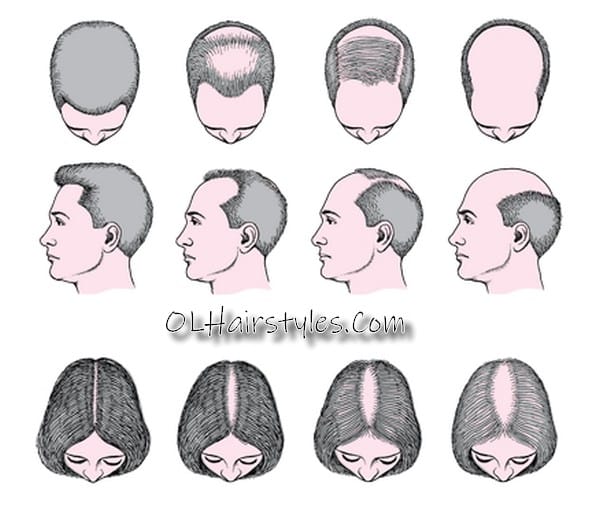

Androgenic alopecia and symptoms
- Excessive hair loss
- Reduced regrowth of hair
- Miniaturization: the original hair is usually replaced by a smaller, thinner successor. (below in the video!)
Androgenic alopecia affects almost 30% of men before the age of 30 and 50% over the age of 50. 40% of women over 50 also suffer from it.
androgenic alopecia symptoms
Causes of androgenetic alopecia
The causes of androgenic alopecia are not clear to this day, although according to the name, it is widely believed that it includes a hormonal (androgen) as well as a genetic predisposition.
Of all the hormones affecting human hair, androgen has the greatest influence.
Doctors consider an increased amount of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the body and scalp to be the main cause of AA. Dihydrotestosterone is a derivative of male testosterone that is responsible for shrinking the hair follicles on the head.
Testosterone is converted to DHT in the body by the enzyme type II 5-alpha reductase. This is found in the sebaceous glands of the hair follicles. There is a widespread theory that the cause of shrinking hair follicles is not the amount of testosterone in the body’s bloodstream but the level of DHT that binds to receptors in the hair follicles.
WATCH THE VIDEO HOW HAIR GROWTH AND GROWTH FACTORS WORK
What is Dihydrotestosterone?
In men, the DHT hormone is very important for puberty. It is DHT that causes the growth of body and facial hair. However, in later life, it is androgens (mainly DHT) that cause the reduction and shrinkage of hair follicles on the head.
Also, many women notice increased shedding and thinning of hair on the head during pregnancy or menopause. This is again caused by an increased amount of DHT in the scalp.
How does DHT affect hair?
how DHT affects hair
The process of the destructive action of DHT on hair and its cycle can be described in several phases:
- After derivation, highly active dihydrotestosterone binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles.
- Due to the action of DHT, the follicles shrink, which results in thinning of the hair on the head, the so-called miniaturization.
- A hair follicle damaged in this way is no longer capable of producing healthy hair.
The miniaturization process can take several years. Due to the effect of DHT, the hair gradually turns into fine, colorless hair with each cycle or simply falls out.
DHT and the hair cycle
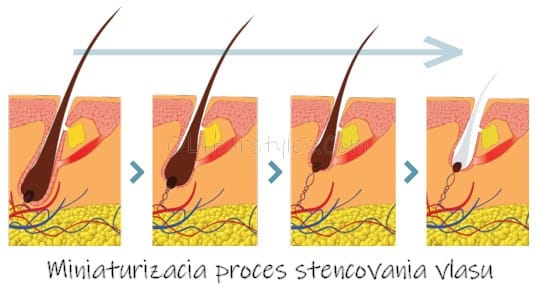
The longer the hair follicle remains in contact with DHT, the more it is squeezed and shrunk by it, causing the hair produced to become thinner, shorter, and lose its color with each hair cycle. DHT also increases the intensity of hair loss by shortening the hair cycle and its growth-anagen phase and causing it to reach the telogen phase prematurely, which accelerates the entire destruction process. The loss of hair is immediately noticeable because, with such a shortened hair cycle, more hair falls out than grows back.
By forcing the hair follicles to reach Telogen faster, the Anagen (growth phase) becomes shorter, which means more and more shedding. If we do not start the treatment, this process continues, and the follicles gradually become smaller and disappear over time.
FAQ on Hair Loss and Forms of Alopecia
Q: What is Androgenetic Alopecia?
A: Androgenetic alopecia is also known as male or female pattern baldness. It’s quite in adults and usually happens slowly over time. Genetics play a big role, so if your has it, you might too. Seeing your hair thin out can be really stressful and make you worry about how you look.
Q: What does Alopecia Totalis mean?
A: Imagine waking up one morning to find that your head is completely bare! That’s a big change and can be pretty shocking. Many people feel different about themselves after experiencing this kind of hair loss.
Q: What is Alopecia Universalis?
A: If you’re dealing with any type of hair loss, remember that you’re not alone.

Leave a Reply